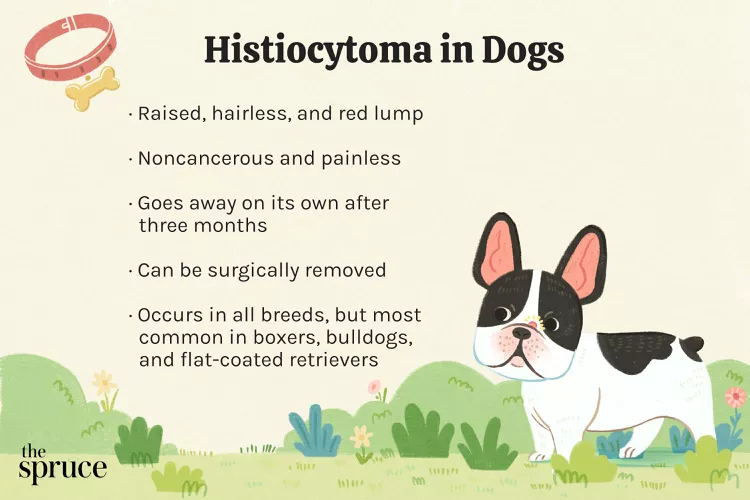
Histiocytomas look scary but they are not dangerous. Raised, red, and sometimes ulcerated, these benign growths are not usually painful or itchy for dogs. Surgical treatment is only recommended if the bump grows large enough to bother the dog or the owner. There are similar bumps that can indicate parasites or malignancy, though, so a veterinary exam is recommended to verify the type of growth on your dog's skin.
A histiocytoma is a type of benign (non-cancerous) skin growth typically seen in young dogs. They originate in the Langerhans cells (also called histiocytes), which help protect a dog's body from foreign "invaders" on the skin such as pollen, bacteria, or fungi.
Histiocytomas most commonly occur in dogs three years of age and younger. They generally appear suddenly and are discovered by chance when owners are petting their dogs. Because histiocytomas cause little or no irritation, dogs generally will not alert owners to them by scratching, licking, or chewing.
These growths are raised and usually smooth-surfaced, giving them a button-like appearance. They typically appear on the head, neck, ears, or limbs of a dog but can occur elsewhere on a dog's body. They can be as large as four centimeters in diameter but tend to be less than two centimeters.
Histiocytomas can occur in any breed of dog, but some breeds that they are more commonly seen in include boxers, bulldogs, and flat-coated retrievers.
While histiocytomas themselves are non-cancerous, on a microscopic level, they belong to a broader classification of growths known as round-cell tumors. There is no known cause for these tumors, some of which can become cancerous.
If your dog suddenly develops a lump, or you suspect your dog may have a histiocytoma, your veterinarian will start by performing a thorough exam and obtaining a history of your dog.
As with all growths, definitive diagnoses of the type of growth are done by looking at the cells microscopically. This is accomplished either by surgically removing the growth and biopsying it or performing something called a fine needle aspirate, or FNA. An FNA is performed by collecting cells from the growth on a needle and then transferring them to a slide to look at under the microscope. It is minimally invasive and can be done on the same day as your initial exam for the growth.
If the growth is located in an area that would make aspirating or biopsying difficult and there is a high suspicion of a histiocytoma, your vet may opt to wait on performing any diagnostics and watch the lump to see if it remains stable or resolves on its own.
Once your vet has definitively diagnosed your dog's lump as a histiocytoma, you can discuss removal options. Your vet may recommend waiting to see what the growth looks like in a few weeks or months. It is not uncommon for histiocytomas to resolve on their own.
Although these types of growths are rarely painful or irritating to a dog, it is important to prevent dogs from licking, chewing, or scratching, which may create secondary infections.
If the growth does not disappear, your vet may recommend removal via cryosurgery. This involves a local anesthetic to the area to freeze the growth. If your dog's histiocytoma is large, then cryosurgery may not be possible, so surgical removal will be the best option.
If your dog has a histiocytoma surgically removed, as with all post-surgery care, it is of the utmost importance to prevent your dog from licking, chewing, or scratching at the incision to prevent him/her from opening up the incision and/or creating a secondary infection. Your vet will provide specific post-surgery instructions to keep the incision area clean.
If you notice any significant redness, swelling, or missing stitches, or if the incision feels warmer than the surrounding tissue, be sure to notify your vet immediately.
Dogs generally recover quickly from this minor surgery and suffer no long-lasting effects from the procedure. Dogs with small, painless histiocytomas may live happily with these benign growths for many years—no surgery required.
Because histiocytomas have no identifiable cause, there is no way to prevent them from growing. They are not contagious, though, and cannot be spread through skin-to-skin contact. They do not pose any threat to any humans or any other animals that your dog may come into contact with.

Cute Pictures & Facts About Calico Cats & Kittens
Learn fascinating facts about calico cats, including photos, the genetics behind this color combination, and common folklore and traditions.
How to Prevent Cat Separation Anxiety During Vacations
Discover why cats develop litter box problems and cat behavior problems when you go on vacation and what you can do about it to help them.
Cat Behavior Changes That Might Mean Something's Wrong
Cats' behavioral changes may indicate problems—or they may mean nothing at all. Explore causes of odd behavior and what to do about them.
Lhasa Apso: Dog Breed Characteristics & Care
The Lhasa apso is an ancient breed from Tibet that was bred to be a watchdog. Learn about its history, health, exercise needs, and more.
Reasons Why Dogs Run Away and How to Stop It
Dogs can escape, especially if they’re bored and not properly contained. Here are some techniques for stopping your dog from running away.
Can Dogs Get Depression? How to Help Your Sad Dog
Can dogs get depression? Learn about the signs of depression in dogs and find out how to help your sad dog.
How to Stop Aggression in Dogs
Dog aggression can be a serious behavior issue for pet owners. Learn how to stop aggression in dogs before someone gets hurt.
How to Stop Your Dog From Growling
A growling dog can soon become even more aggressive. Reduce the noise and potential for a dangerous situation with some of these techniques.
Why Do Dogs Dig Holes? How to Stop Your Dog from Relandscaping Your Yard
Dogs have been digging holes for centuries and for many reasons. Whether they’re bored or want to cool off in the dirt, here are the top reasons why dogs dig holes.
Dog Treat Varieties
Learn about the different types of dog treats on the market and decide which are best for your dog.
Can Dogs Eat Asparagus?
Dogs can eat asparagus, provided the vegetable is cooked plain and cut up for them. Seasonings, salt, and butter make it unhealthy for dogs.
Histiocytomas in Dogs
A histiocytoma is a type of benign (non-cancerous) skin lump that usually affects young dogs. Learn the causes, treatment, and prevention.
Why Is My Dog’s Eye Swollen?
If your dog's eye is swollen, she may need veterinary attention. The inflammation could be caused by allergies, an injury, or even a tumor.
Common Bugs and Parasites Found on and Inside Dogs
Learn about common types of parasites in dogs. Find out how to treat and prevent parasites to keep your dog, your family, and yourself safe.
Exploring the Different Types of Pet-Friendly Beaches
Are you looking for pet-friendly beaches? Learn about the different types of pet-friendly beaches, their locations, and tips for visiting them with your pet.
10 Obscure, Little-known Canine Facts in Honor of National Dog Day
With National Dog Day upon us, it's time to celebrate everything about our favorite pets—even the weirder stuff. Here are 10 obscure facts about dogs you probably didn't know.
Kitten Development From 3 to 6 Months Old
Kittens grow and change a lot during their first year. Find out what happens between the ages of three months and six months old.
95 Siamese Cat Names
Our list of Siamese cat names has diverse and fun options to help you choose the ideal moniker for your elegant and lovable feline companion.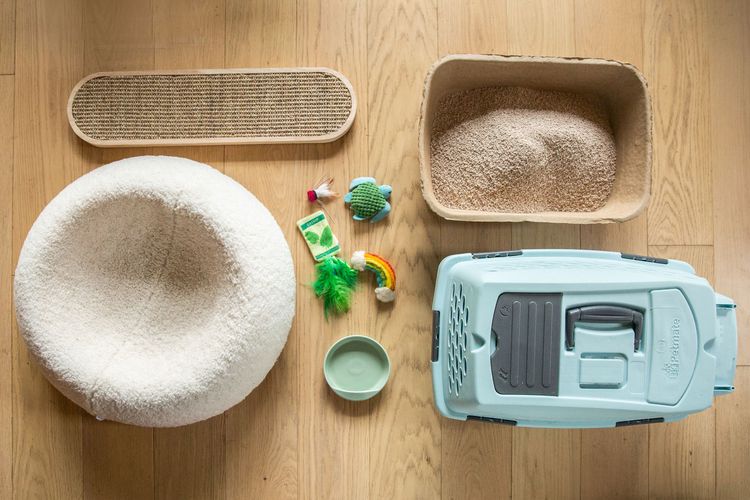
What to Buy for Your New Cat: A List of Essentials
Before you bring your new cat or kitten home, there are a number of things to collect or buy so your cat will feel welcomed like a family member.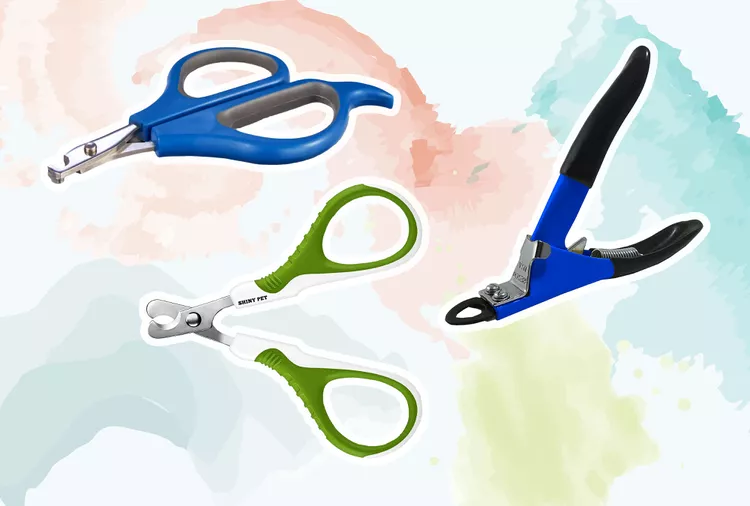
The 6 Best Cat Nail Clippers of 2024 for a Safe Trim
Clipping your cat's nails can save your furniture and keep your kitty comfortable. We asked veterinarians for their cat nail clipper recommendations.